Spark Streaming是core Spark API的扩展,实现可扩展(scalable),高吞吐量(high-throughput),容错的实时数据流的流式处理。数据可以从多种数据源如kafka、flume等灌入,而且可以使用带有高级函数如map、reduce、join和window的复杂算法来处理。实际上,你可以在数据流上使用spark的机器学习和图处理算法。
spark streaming接收数据,然后把它切割成batches,如下图
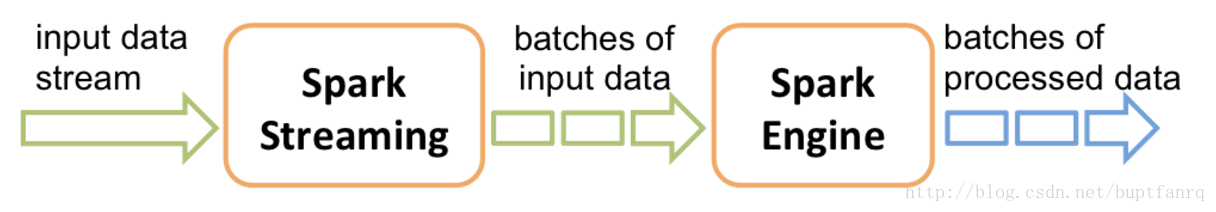
Spark Streaming 将其抽象为离散流或者DStream,代表了连续的数据流。Dstream的本质是一连串的RDDs
窗口操作
一个滑动的窗口,两个因素:窗口大小和滑动尺寸
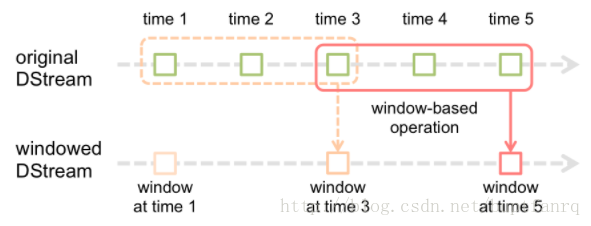
例子
|
|
使用foreachRDD的设计模式
功能很强大,使用需谨慎!
使用它的时候一般是输出到外部数据源的时候,此时需要与数据源建立connection
错误的使用方式
关注注释,因为connection对象是不可序列化的,这会导致序列化错误。
|
|
低效的使用方式
在worker端每一个rdd都创建连接,很明显这个是低效而且愚蠢的方式。连接是很昂贵的资源。
|
|
浪费的使用方式
相比于前者,扩大了范围rdd->partition
|
|
正确的使用方式
使用连接池
|
|
参考
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-programming-guide.html